Mahoning County Auditor Property
Mahoning county auditor property On April 4, 2025, Auditor Meacham hosted a Property Tax Relief Briefing in the Community Room of the Covelli Centre.
A bipartisan group of county auditors in conjunction with the County Auditors’ Association of Ohio (CAAO) addressed local media outlets to advocate for legislative proposals that could provide relief to Ohio homeowners.
Montgomery County Auditor Karl Keith, Lorain County Auditor Craig Snodgrass and Lake County Auditor Chris Galloway joined Auditor Meacham in presenting appraisal and property tax data on their respective counties. District 65 State Representative Dave Thomas presented information on the property tax relief proposals.
The County Auditor plays the vital role of Fiscal Officer of the County with oversight responsibility of all financial books and records of all county offices.
What does a county auditor do in Ohio
In Ohio, the County Auditor is the chief fiscal officer for the county, responsible for a wide range of duties related to financial management and property tax administration. They oversee all county financial records, manage payroll, and ensure accurate property tax valuations.
A county auditor’s primary role is to oversee and ensure the proper management of county financial records and resources, acting as a key internal accounting and fiscal officer. They are responsible for maintaining accurate financial records, preparing budgets, assisting with tax duties, and ensuring the county’s financial integrity.
The specific duties of a county auditor can vary slightly depending on the size of the county and the specific requirements of the state. In smaller counties, the county clerk may also act as the county auditor.

Key Responsibilities of an Ohio County Auditor:
Chief Fiscal Officer:
Auditor The is responsible for the county’s finances, including keeping records, paying bills, and managing payroll.
Property Tax Assessment:
The Auditor is the statutory appraiser-in-chief for all real estate and manufactured homes in the county, ensuring fair and uniform valuations for tax purposes.
Tax Distribution:
The Auditor distributes collected property taxes to various local governments like cities, villages, townships, and school districts.
Sealer of Weights and Measures:
The Auditor oversees the enforcement of laws related to weights and measures, ensuring accuracy of scales and other measuring devices used in retail and industry.
Licensing Agent:
The Auditor issues licenses for various activities, including dogs, kennels, vendors, and cigarettes.
Financial Reporting:
The Auditor prepares the county’s annual financial report and ensures proper financial record-keeping.
Special Assessments and Refunds:
The Auditor administers special assessments on property and manages tax refunds and abatements.
Homestead Exemption and Other Tax Credits
The Auditor administers the homestead exemption program and other property tax credits.
Tax Levies:
THE Auditor calculates and certifies tax levies, such as those for bonds and emergency situations.
Why have a County Auditor
County government was created in the Constitution of 1876, and subsequently, it was determined that county government needed a system of checks and balances so as to ensure no one branch of government would be without accountability in complying with the State’s statutes. In response to addressing a need of checks and balances, the position County Auditor emerged years later in 1905. There are many reasons to have a County Auditor, but the main one is to maintain the integrity of financial administration in county government. The County Auditor, by law, has oversight of all financial books and records of all officers of the County and is charged with administering the budget. Commissioners Court, by law, is the governing and administrative body in county government. Among the many duties of Commissioners Court is the power to determine the county budget and make appropriations of funds to meet that budget. Both the County Auditor and Commissioners Court are required, by law, to approve or reject claims for disbursement of county funds. Simply put, the integrity of county financial administration is entrusted to a dual control system of “checks and balances.” This system works, not just because there is a County Auditor and not just because there is a Commissioners Court; it works because neither has creative or authoritative control over the other. I
Ohio Property Tax Rates
| County | Median Home Value | Average Effective Property Tax Rate |
| Lorain County | $191,900 | 1.51% |
| Lucas County | $144,200 | 1.82% |
| Madison County | $201,200 | 1.14% |
| Mahoning County | $132,000 | 1.47% |
How property Taxes are calculated
Under Ohio law, the Auditor determines a fair market value for each property – an agreed upon price between a willing buyer and seller in the open market.
The Treasurer collects taxes based on property value and current tax rates (millage).
Taxes are determined by voters. The following lists the formulas that the State of Ohio has authorized for the calculation of property taxes.
Market Value x 35% = Assessed Value
Example: $100,000 x .35 = $35,000
(Assessed Value x Tax Rate)/1000 = Current Real Estate Tax/Year
Example: ($35,000 x 99.51)/1000 = $3,482.85
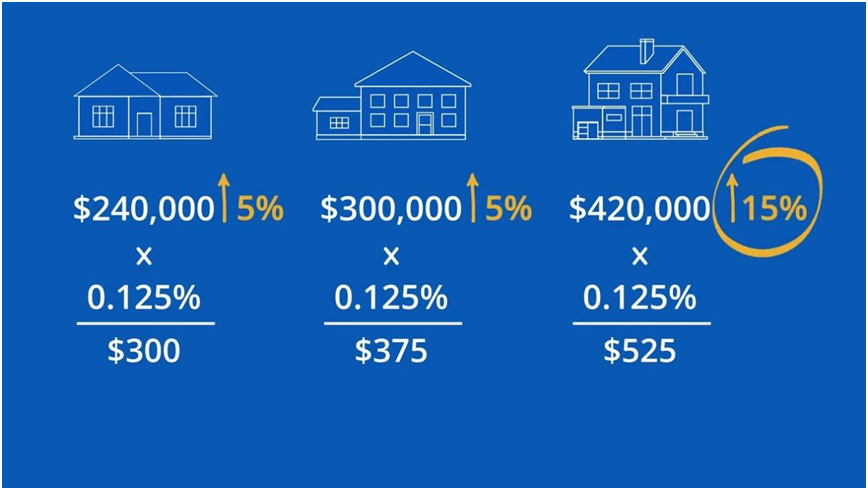
List of current and previous Tax Rates for Lucas County.
Current Tax x Reduction Factors = Reduction Credits
Provided by Ohio Law
Current Tax – Reduction Credits = Tax Subtotal
Tax Subtotal – Non-Business Credit = Net Taxes Per Year
Owner Occupied Credit
Net Tax + Special Assessments = Total Taxes Per Year
(if applicable)
Total Tax / 2 = Current Half Tax Due

Which county in Ohio has the cheapest property taxes
The average effective property tax rate in Ohio is 1.43%. However, tax rates vary significantly between Ohio counties and cities. The highest rates are in Cuyahoga County, where the average effective rate is 2.18%. The county with the lowest rate is Noble County, which has an average effective rate of 0.83%
Mahoning county highest and lowest rates
In Mahoning County, the highest median listing home price is in New Middletown at $400K, while the most affordable is in Youngstown at $119.9K. The Median property value in 2023 was $141,100. The median household income in 2023 was $55,576.
Elaboration:
- Real Estate: New Middletown stands out as the most expensive place to buy a home in Mahoning County, with a median listing price of $400,000. Youngstown, on the other hand, offers the most affordable housing options, with a median listing price of $119,900.
- Median Property Value: The median property value in Mahoning County as a whole is $141,100, which is significantly lower than the national average.
- Median Household Income: The median household income in the county is $55,576
How I pay Taxes online in OHio
Pay Ohio Property Taxes Online & On timemakes it easy to pay Ohio property taxes using your favorite debit or credit card. It’s fast, easy & secure, and your payment is processed immediately. It is easy and fast way to do work . By doing online paying texes you can save your time, energy and other deus